How can we work together to reach the status of high-technology nation?
Malaysia was ranked 8th in Asia and 33rd globally in 2020 by the Global Innovation Index (GII); 2nd in Asia and 26th globally by the IMD World Digital Competitiveness Ranking 2020; and 11th globally by Startup Genome as a burgeoning start-up ecosystem in 2020. (2020). Despite the classification’s recognition of Malaysia’s competitiveness, much more work need to be done to restore Malaysia’s prior standing as an Asian Tiger.
The current economic and political conditions in Malaysia lead some pessimists to infer that the country will "NOT" achieve the status by 2030; on the other hand, there is still a considerable number of optimists who believe that we can make a difference. According to the results of a survey conducted through a public Facebook group called "Entrepreneurs and Startups in Malaysia" with approximately 56.3k members, there are a few critical measures that must be implemented in order to foster a favorable ecosystem in order to achieve the stated objective.
Prior to COVID-19, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) accounted for 98.5 percent of all business establishments in Malaysia, accounting for around 38.9 percent of our Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and employing over 7.3 million people nationwide (48.4 percent of total employment). Focusing on small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is essential for achieving this goal since they are far nimbler in adopting sophisticated technology and may be pushed to steer the economy in the desired direction. The continued use of commodities would place us in a difficult position, particularly in the semiconductor industry, as we would have an uphill battle to compete with countries that have a competitive advantage, such as Indonesia and Vietnam, where labor costs are significantly lower. However, since the majority of SMEs in Malaysia are family-owned and controlled by persons between the ages of 50 and 60, a well-defined plan is required to encourage them to take on the task. Undoubtedly, one of the initiatives to promote growth will be to implement a program that awards business loans and grants solely based on merit.
Additionally, it is critical for our economy to transition to a more skilled service sector, which may be accomplished by boosting our innovation pipeline. To accomplish this :
- Identify areas where Malaysia has a competitive advantage and then work to maintain that advantage. Our innovation pipeline is now experiencing a number of barriers that require the immediate attention of key stakeholders, including a lack of data availability and accessibility.
- The talent pipeline must be scrutinized. A thorough revamp of our educational system to ensure that people (particularly the young adult population) receive adequate training in certain technologies (by a combination of theory and practice) would be a critical first step.
- A comparative review of how other countries have carried out their high-technology transformation programs will also be beneficial to Malaysia because it will allow it to learn from their successes as well as their errors in the process. It follows that reaching high technology nation status, as with other national objectives, is dependent on the implementation of structural changes mentioned in SPV2030, such as strong government, high integrity, and transparency between the government and the rakyat. Bribery must be eliminated at all levels, and enhanced interaction with industry stakeholders is required to guarantee that inclusive techniques are used in the pursuit of this aim.
This led in the establishment of the High-Tech Council, which reports directly to the Prime Minister-chaired National Science Council, and which represents a significant step forward in the government's attempts to solve these issues. Establish and stick to SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) goals throughout the process of becoming a high-technology nation, and Malaysia will be much stronger on its journey to becoming a high-technology nation sooner rather than later.
Finally, Malaysians must always support Malaysians during the process of realizing this attainable objective. Instead of being harmful, criticisms should be beneficial. The spirit of "cooperation" among the government, industrial actors, academics, and the Rakyat in embracing technology is critical for Malaysia to remain competitive in the area and eventually become a high-income nation.
Mobile Applications For Sustainability of Small And Medium Enterprise (SME) Industry In Future Post Covid-19
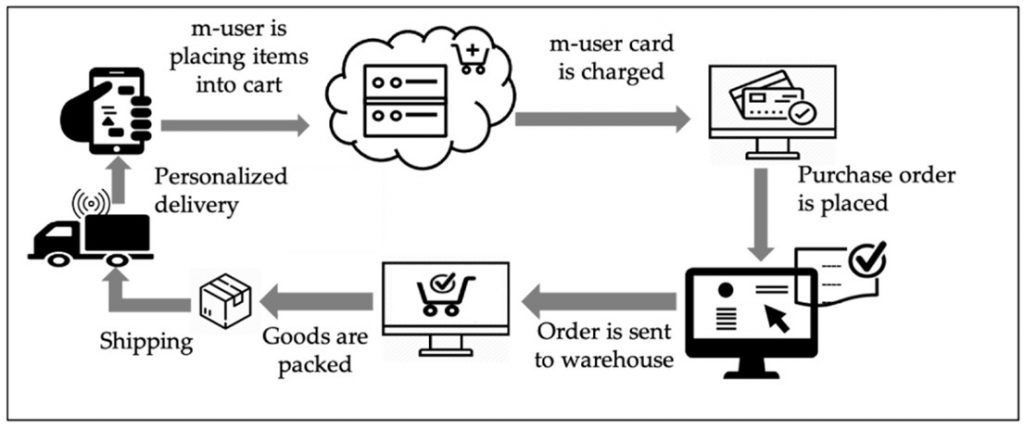
Aside from the impact on public health, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused a significant economic shock. As contrary to large businesses, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) have been hardest hit by the COVID-19, due to most SME industries like retail and services are rely on a traditional business model, whereby involving human-to-human interaction. To sustain the SME industry in future post Covid-19, the SME companies have to develop a novel approach in their business model. Hence, this study proposes a development of mobile application in the SME’s business model. The widespread use of mobile phones in all aspects of life, as well as the advancement of mobile technology, enable the SME industries to thrive. The proposed approach allows the SMEs to liaise with customers faster than traditional business models (at any time and from any location without any physical contact) yet improves customer engagement, broaden the audience reach and boost brand recognition. Moreover, it also improves the operations of SMEs, such as cost and employee productivity, while also ensuring their long-term viability. However, SME applications must communicate with the company's back-end systems, which requires considerable development.
Cyber Security Threat Analysis in Higher Education Institutions during Covid-19 Pandemic
Aside from the impact on public health, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused a significant economic shock. As contrary to large businesses, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) have been hardest hit by the COVID-19, due to most SME industries like retail and services are rely on a traditional business model, whereby involving human-to-human interaction. With the development of mobile applications (mobile apps), SME industries could be revived and thrived. SME industries are significantly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. Most of SME companies unable to sustain since their business model is carried out using a traditional method; human-to-human interaction. To sustain the SME industry in future post Covid-19, the SME companies have to develop a novel approach in their business model. Hence, this study proposes a development of mobile application in the SME’s business model. The widespread use of mobile phones in all aspects of life, as well as the advancement of mobile technology, enable the SME industries to thrive. The proposed approach allows the SMEs to liaise with customers faster than traditional business models (at any time and from any location without any physical contact) yet improves customer engagement, broaden the audience reach and boost brand recognition. Moreover, it also improves the operations of SMEs, such as cost and employee productivity, while also ensuring their long-term viability. However, SME applications must communicate with the company's back-end systems, which requires considerable development.
E-Commerce and Mobile Apps: Opportunities for SMEs in Developing Countries

From grab to shoppee, mobile applications are transforming the way businesses are conducted, offering multiple new revenue streams and market opportunities. Asset sharing has become a reality because of technological advancements, enabling more efficient resource utilization at considerably lower prices than previously thought conceivable. Markets are becoming increasingly interconnected, and communication is engrained in the way we conduct business. Many researchers studied an overview of current e-commerce and mobile application principles. The finding implies that e-commerce is reliant on e-commerce technologies to a substantial extent. Adoption of technology is becoming more inexpensive and a requirement for survival in today's ultra-competitive business environment. Only brick-and-mortar firms or those without an online presence would be significantly disadvantaged and may even close sooner rather than later. The adaptability of SME businesses makes it easier to make large-scale decisions, such as adopting new technology or altering or even completely overhauling an existing company process to satisfy market needs and capitalize on present or potential opportunities. E-Commerce, on the other hand, enables SMEs to significantly increase their profits by putting their products at the fingertips of millions of potential buyers worldwide.
